What Is Shockwave Therapy?
– Stuti Punshi
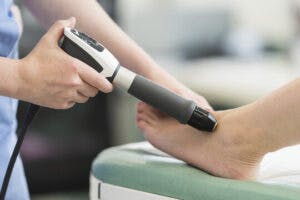
Shockwave Therapy (SWT), also known as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT), is a modern, non-invasive treatment that uses high-energy sound waves to relieve pain and support healing—especially in areas of chronic pain or injury.
It works by sending focused sound waves into the body to break down soft tissue calcifications, encourage new collagen production, release natural healing chemicals (called growth factors), and activate the body’s natural repair process. This can reduce pain and help you stay active without surgery or long recovery times.
Originally used in the 1980s for treating kidney stones, shockwave therapy has since become a proven treatment in orthopedics. Research shows it can help reduce pain and boost healing in bones, tendons, ligaments, and fascia. It’s also been found helpful for some neurological conditions to reduce muscle tightness (spasticity).
How Does It Work?
Shockwave therapy uses powerful sound waves with very specific features. Each wave is extremely fast and short—lasting just a few milliseconds. But within that time, a lot happens!
Each shockwave has two parts:
- The first part delivers a strong push into the tissue—like a precise tap that creates mechanical pressure.
- The second part creates tiny bubbles in the tissue. These bubbles rapidly collapse (a process called cavitation), sending out even more energy into the area, which helps amplify healing.
This effect is kind of like a controlled explosion—similar to the sonic boom from a jet or the crack of thunder after lightning. Compared to something like ultrasound, shockwaves are much more intense, delivering about 1,000 times more pressure.
This powerful combination improves blood flow, reduces inflammation, and encourages tissue regeneration. It’s especially effective in areas that don’t get good blood supply on their own, like tendons and ligaments.
What Does the Research Say?
Studies show that ESWT can deliver mechanical forces deep into tissues, which stimulates blood flow and metabolism. This is especially useful for tendons, which naturally get very little blood supply and often take a long time to heal.
Shockwaves mimic some of the natural forces the body experiences during activity or injury—helping to “wake up” the healing response and promote tissue repair, even in stubborn or long-term injuries.
What Is Shockwave Therapy Used For?
Shockwave therapy is used to treat a variety of common injuries and conditions, especially those involving tendons, ligaments, and bones. These include:
- Plantar fasciitis
- Achilles tendinopathy (mid-portion and insertional types)
- Patellar tendinopathy (jumper’s knee)
- Proximal hamstring tendinopathy
- Hip pain (greater trochanteric pain syndrome, bursitis)
- Golfer’s elbow
- Tennis elbow
- Calcific tendinopathy
- Shin splints (MTSS)
- Stress fractures and non-healing fractures
Does It Hurt?
That depends! Most patients describe the treatment as uncomfortable but manageable—not exactly painful. More sensitive areas (like over a bone) may feel sharper, while areas with more muscle tend to be easier to tolerate.
We always adjust the intensity to match your personal comfort level. The goal is to reach a 5 out of 10 on your pain scale—not more.
What to Expect During a Shockwave Session
When you come in for treatment:
- Wear clothing that allows easy access to the area we’ll be treating. We also provide gowns or disposable shorts if needed.
- We’ll position you comfortably and apply a water-based gel to help conduct the sound waves.
- A handheld applicator is then moved over the area, releasing controlled pulses of pressure waves. We’ll slowly increase the intensity until we reach your ideal therapeutic level.
- A typical session includes around 2,000 pulses and takes about 15 minutes.
Most people feel some relief right away, and many only need 2–3 sessions over 6 to 12 weeks for lasting results.
What Happens After the Treatment?
It’s normal to feel a bit sore or have light bruising around the treatment area afterward. That’s a sign your body is starting to heal.
Avoid taking anti-inflammatory medications like Advil (ibuprofen) for a day or two, as inflammation is part of the healing process we’re trying to stimulate.
Other than that, you can go about your day as usual—including exercise if you feel up to it.
Ready to Learn More or Book a Session?
If you’d like to learn more about how shockwave therapy can help you, or you want to book a treatment session, feel free to reach out:
📞 Call: 647-496-7065
📧 Email: completecarels@gmail.com
One of our clinicians will be happy to discuss your treatment options and answer any questions you may have.



